In today's rapidly evolving digital landscape, establishing a robust IT governance and compliance framework is no longer optional—it's imperative. This comprehensive guide equips IT leaders with the knowledge and strategies to build and refine their IT governance and compliance frameworks, covering core concepts, leading frameworks, governance structures, policy development, risk management, and regulatory compliance.
Introduction
In today's rapidly evolving digital landscape, where technological advancements and regulatory demands are constantly shifting, establishing a robust IT governance and compliance framework is no longer optional—it's imperative. For enterprise organizations, this framework is the bedrock upon which data security, regulatory adherence, business continuity, and effective risk mitigation are built.
As Chief Information Officers (CIOs) and IT leaders navigate this complex environment, the ability to strategically align technology with overarching business objectives while simultaneously mitigating risks and adhering to a myriad of regulations (such as GDPR, HIPAA, and the Philippine Data Privacy Act) becomes paramount.
Recent reports underscore this necessity: a 2023 Gartner study revealed that organizations with strong IT governance achieve significantly better business outcomes, yet only a fraction have fully mature frameworks.
The consequences of poor governance are stark, ranging from devastating security breaches and hefty regulatory fines to crippling operational disruptions. Conversely, a well-implemented framework delivers tangible benefits: enhanced data security, seamless regulatory compliance, resilient business continuity, and proactive risk mitigation.
🏛️1. Understanding IT Governance and Compliance
To effectively build and manage an IT governance and compliance framework, it's crucial to first grasp the fundamental definitions and the symbiotic relationship between these two critical components.
1.1 What is IT Governance?
IT governance is the formal system of processes, policies, and structures that directs and controls how an organization's information technology supports and extends its business strategy. It is about ensuring that IT investments deliver value, manage risks effectively, and align with organizational goals, all while fostering transparency and accountability across IT operations.
At its core, IT governance addresses key questions such as:
- What decisions need to be made to ensure effective management of IT?
- Who should make these decisions?
- How will these decisions be made and communicated?
- How will performance be monitored?
Effective IT governance typically encompasses five critical domains:
- Strategic Alignment - Ensuring that IT strategy and operations are seamlessly integrated with the overall business strategy, so IT initiatives directly support business goals
- Value Delivery - Focusing on ensuring that IT investments yield measurable value for the business, optimizing costs, enhancing efficiency, and fostering innovation
- Resource Management - Optimizing the efficient and effective utilization of all IT resources, including human capital, technology infrastructure, applications, and data
- Risk Management - Proactively identifying, assessing, mitigating, and monitoring IT-related risks to protect organizational assets and ensure business continuity
- Performance Measurement - Continuously tracking and monitoring IT performance against predefined goals and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to assess effectiveness and drive continuous improvement
1.2 What is IT Compliance?
IT compliance, while closely related to governance, focuses specifically on an organization's adherence to applicable laws, regulations, and industry standards related to its IT systems and data. It is about meeting external and internal mandates to avoid legal penalties, financial fines, and reputational damage.
Key examples of regulatory frameworks driving IT compliance include:
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) - A comprehensive data privacy law in the European Union that sets strict rules for how personal data is collected, processed, and stored
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) - A U.S. law that mandates security and privacy standards for protected health information (PHI)
- Philippine Data Privacy Act (DPA) - A law in the Philippines that protects the fundamental human right to privacy of communication while ensuring the free flow of information to promote innovation and growth
- ISO/IEC 27001 - An international standard for information security management systems (ISMS) that provides a systematic approach to managing sensitive company information
1.3 The Synergy: Why Both are Essential
IT governance and compliance are not isolated concepts; they are two sides of the same coin, forming a synergistic relationship that is vital for organizational success. Governance provides the overarching structure and processes that enable an organization to achieve and sustain compliance.
Without strong governance, compliance efforts can become fragmented, reactive, and unsustainable, leading to a perpetual cycle of addressing audit findings rather than proactively managing risks. The consequences of neglecting either aspect are severe:
- Security Breaches - Weak governance practices are often linked to a higher incidence of data breaches, leading to significant financial losses and erosion of customer trust
- Regulatory Fines - Non-compliance with regulations can result in substantial penalties, as seen with GDPR fines that can reach millions of Euros or a percentage of global annual revenue
- Operational Disruptions - A lack of robust IT governance can lead to prolonged downtime and significant costs during system failures or cyberattacks
📚2. Key IT Governance Frameworks and Standards
To establish a robust IT governance and compliance framework, organizations often leverage established frameworks and standards. These provide a structured approach, best practices, and a common language for managing IT.
2.1 COBIT 2019: Comprehensive Enterprise IT Governance
COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies) 2019 is the most comprehensive framework for enterprise IT governance and management, developed by ISACA. It provides a holistic approach that integrates various frameworks, standards, and practices.
Key Principles of COBIT 2019:
- Provide Stakeholder Value - Focuses on generating value from I&T investments for all stakeholders
- Holistic Approach - Considers all relevant components including processes, organizational structures, culture, ethics, and information
- Dynamic Governance System - Adapts to changes in the enterprise and its environment
- Governance Distinct From Management - Clearly differentiates between governance (ensuring objectives are achieved) and management (planning, building, running, and monitoring activities)
- Tailored to Enterprise Needs - Allows for customization based on the enterprise's specific context, priorities, and risk appetite
- End-to-End Governance System - Integrates I&T governance into overall enterprise governance
COBIT 2019 - 40 Governance and Management Objectives:
COBIT 2019 defines 40 governance and management objectives, grouped into five domains:
| Domain | Focus Area | Key Objectives | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Evaluate, Direct and Monitor (EDM) | Governance oversight | 5 objectives | EDM01: Governance Framework Setting, EDM05: Stakeholder Transparency |
| Align, Plan and Organise (APO) | Strategic alignment and planning | 14 objectives | APO01: IT Management Framework, APO13: Managed Security |
| Build, Acquire and Implement (BAI) | Solution development and implementation | 11 objectives | BAI01: Managed Programmes and Projects, BAI11: Managed Projects |
| Deliver, Service and Support (DSS) | Operational service delivery | 6 objectives | DSS01: Managed Operations, DSS06: Business Process Controls |
| Monitor, Evaluate and Assess (MEA) | Performance monitoring and compliance | 4 objectives | MEA01: Performance Assessment, MEA03: Compliance Monitoring |
COBIT 2019 Governance System Components:
COBIT 2019 identifies six types of components that constitute a governance system:
Processes
Describe a set of practices and activities to achieve certain objectives and produce a set of outputs in support of overall IT goals
Organizational Structures
Key decision-making entities in an enterprise, including committees, teams, and individual roles
Principles, Policies and Frameworks
Translate desired behavior into practical guidance for day-to-day management
Information
Pertains to all information produced and used by the enterprise, including data quality and information architecture
Culture, Ethics and Behavior
The individual and collective behavior of people in an organization, including leadership and communication
People, Skills and Competencies
Related to people and the skills needed for good decision-making and successful completion of activities
2.2 ITIL 4: Service Value System Excellence
ITIL 4 (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) is a flexible and adaptable framework for IT service management that helps organizations navigate digital transformation and deliver value through the Service Value System (SVS).
ITIL 4 Guiding Principles:
These seven principles guide organizations in all circumstances:
- Focus on value - Everything the organization does should directly or indirectly contribute to value for stakeholders
- Start where you are - Consider what is already available and can be used rather than starting from scratch
- Progress iteratively with feedback - Organize work into smaller, manageable sections that can be executed and completed in a timely manner
- Collaborate and promote visibility - Work across boundaries and ensure transparency to foster shared responsibility
- Think and work holistically - All components work together to deliver value; no service stands alone
- Keep it simple and practical - Use the minimum number of steps necessary to achieve the objective
- Optimize and automate - Automate where possible to maximize efficiency and human effort
ITIL 4 Service Value Chain Activities:
ITIL 4 Management Practices (34 Total):
| Category | Practice Count | Key Examples | Focus Area |
|---|---|---|---|
| General Management Practices | 14 practices | Strategy Management, Portfolio Management, Risk Management | Business management adapted for service management |
| Service Management Practices | 17 practices | Incident Management, Problem Management, Change Enablement | IT service management specific practices |
| Technical Management Practices | 3 practices | Infrastructure Management, Software Development, Deployment | Technology-focused practices |
2.2 Choosing and Integrating Frameworks
Selecting the right framework(s) is a strategic decision that should be tailored to your organization's unique context. Consider the following factors:
- Organizational Size and Complexity - Larger, more complex organizations may benefit from comprehensive frameworks like COBIT, while smaller organizations might start with more focused frameworks like ISO 27001
- Industry and Regulatory Environment - Industries with strict regulatory requirements will need frameworks that directly address those mandates
- Strategic Objectives - If the primary goal is service delivery excellence, ITIL might be a strong starting point. If it's overall IT governance and value realization, COBIT is highly relevant
- Current Maturity Level - Some frameworks are better suited for organizations just beginning their governance journey
🏗️3. Establishing Robust IT Governance Structures
Establishing a clear, well-defined IT governance structure is fundamental to ensuring that technology initiatives are aligned with business goals, risks are managed effectively, and accountability is maintained across the enterprise.
3.1 Foundational Principles of IT Governance
Effective IT governance is built upon several core principles:
- Strategic Alignment - Ensuring that IT strategy and operations are seamlessly integrated with the overall business strategy
- Value Delivery - Focusing on ensuring that IT investments yield measurable value for the business
- Risk Management - Proactively identifying, assessing, mitigating, and monitoring IT-related risks
- Resource Management - Optimizing the efficient and effective utilization of all IT resources
- Performance Measurement - Continuously tracking and monitoring IT performance against predefined goals and KPIs
- Transparency and Accountability - Ensuring that all IT governance activities are conducted with transparency and clear lines of accountability
3.2 Common IT Governance Models
Organizations adopt various IT governance models to structure how technology decisions are made and enforced:
- Centralized Governance - A single group or central IT team makes all major IT decisions for the entire organization. Offers strong consistency and control but can limit flexibility
- Decentralized Governance - Individual business units or departments are empowered to make their own IT decisions. Favors speed and innovation but can lead to inconsistent systems
- Federated (Hybrid) Governance - Combines elements of both centralized and decentralized approaches, balancing company-wide standards with localized flexibility
3.3 Key Organizational Components and Roles
Regardless of the chosen model, a well-defined organizational structure with clear roles and responsibilities is essential:
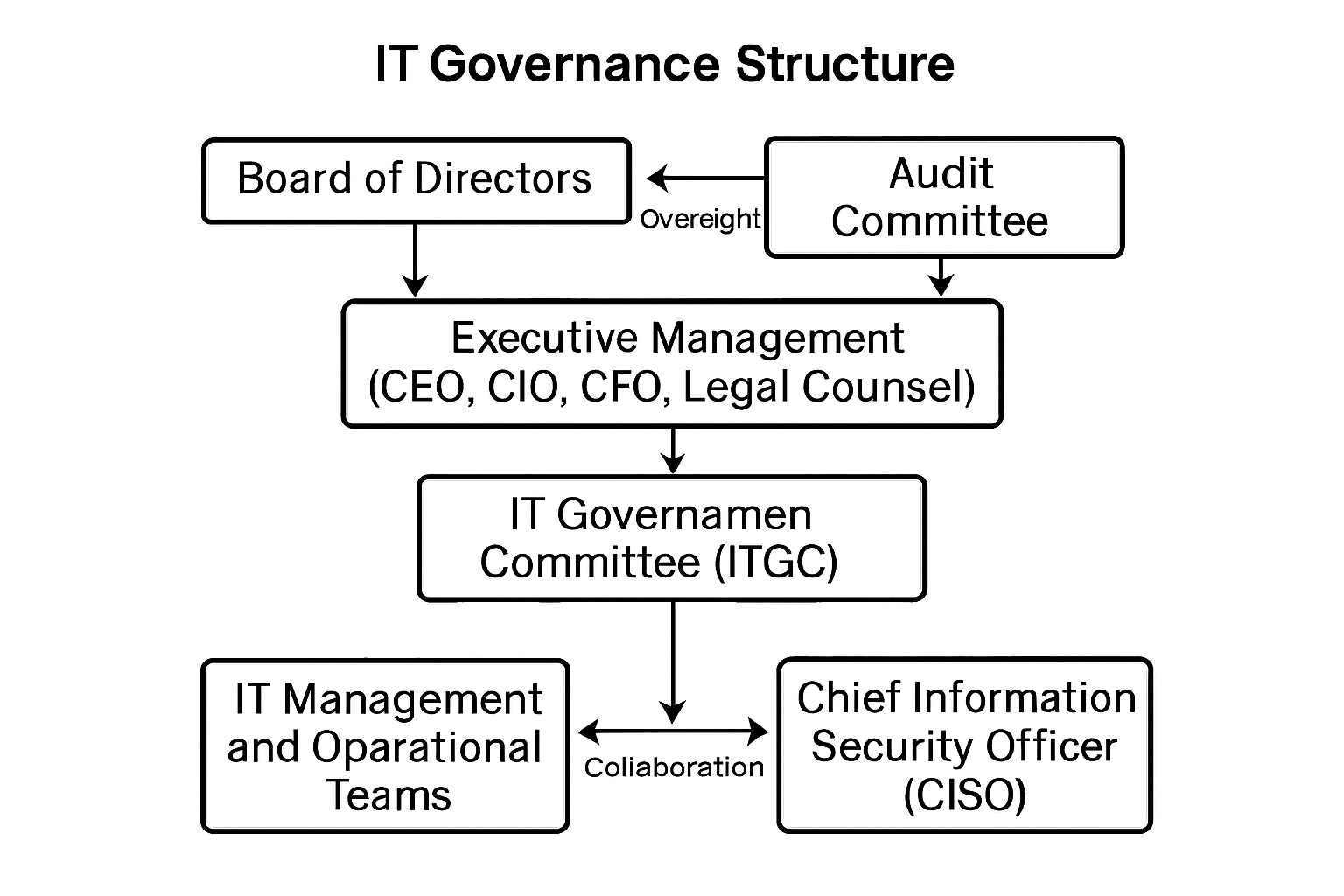
- Board of Directors and Audit Committee - Ultimate fiduciary responsibility, including oversight of IT strategy, performance, and risk management
- Executive Management (CEO, CIO, CFO, Legal Counsel) - Responsible for day-to-day strategic and operational leadership
- IT Governance Committee (ITGC) - Cross-functional body responsible for strategic direction, oversight, and performance monitoring of IT
- IT Management and Operational Teams - Responsible for day-to-day planning, building, running, and monitoring of IT services and infrastructure
- Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) - Primarily accountable for developing and maintaining cybersecurity policies and standards
�4. Developing Effective IT Policies and Procedures
IT policies are the backbone of any robust IT governance framework, serving as formal documentation that communicates required and prohibited activities and behaviors, guiding enterprise operational processes.
4.1 The Importance of IT Policies
Effective IT policies provide several critical benefits:
- Guidance and Clarity - Clear guidelines for employees on how to handle IT resources, data, and systems
- Risk Mitigation - Define acceptable practices and controls, reducing the likelihood of security incidents
- Compliance Assurance - Translate complex regulatory requirements into actionable internal rules
- Operational Efficiency - Standardized procedures streamline IT operations and reduce errors
- Accountability - Establish clear responsibilities and expectations
4.2 Policy Development and Management Lifecycle
The development and management of IT policies follow a distinct lifecycle:
4.3 Essential IT Policy Types
Organizations should develop a comprehensive set of essential IT policy types:
- Acceptable Use Policy (AUP) - Outlines the acceptable and prohibited uses of computer systems, networks, and other IT resources
- Password Management Policy - Establishes guidelines for creating, storing, and managing strong, unique passwords
- Incident Response Policy - Defines the steps and procedures to be followed during a cybersecurity incident
- Data Governance and Privacy Policy - Establishes how data is collected, processed, stored, and protected
- Access Control Policy - Defines who has access to what systems and data, and under what circumstances
- Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery Policy - Outlines procedures for maintaining operations during disruptions
🤝5. Vendor Management and Service Level Agreements
Effective vendor management is crucial for IT governance, ensuring that third-party services meet organizational requirements while managing risks and maintaining compliance. This section provides comprehensive guidance on vendor evaluation, contract management, and service level agreements.
5.1 Vendor Evaluation Framework
A structured vendor evaluation process ensures objective assessment and selection of technology partners. The following comprehensive evaluation matrix provides weighted criteria for systematic vendor comparison.
Vendor Evaluation Categories and Weights
| Evaluation Category | Weight (%) | Key Focus Areas | Assessment Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strategic Alignment | 20% | Business alignment, roadmap compatibility | Vision alignment, future capabilities, scalability |
| Service Availability | 18% | Uptime, reliability, redundancy | SLA guarantees, historical performance, disaster recovery |
| Performance | 15% | Speed, responsiveness, efficiency | Response times, throughput, benchmark results |
| Security | 15% | Data protection, access controls, compliance | Certifications, security practices, incident history |
| Support | 12% | Technical support, account management | Support hours, response times, escalation procedures |
| Financial | 10% | Pricing, cost transparency, value | Total cost of ownership, pricing models, hidden costs |
| Innovation | 5% | R&D investment, future capabilities | Technology leadership, innovation track record |
| Risk Management | 5% | Business continuity, risk mitigation | Risk assessment, mitigation strategies, insurance |
Vendor Scoring Methodology
Each criterion is scored on a scale of 1-5, with specific guidelines for objective assessment:
| Score | Rating | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | Exceptional | Industry leader, exceeds all requirements | 99.99% uptime, 24/7 premium support, innovative solutions |
| 4 | Strong | Above average, meets most requirements well | 99.9% uptime, business hours support, proven solutions |
| 3 | Adequate | Meets basic requirements, acceptable performance | 99.5% uptime, standard support, mainstream solutions |
| 2 | Below Average | Some concerns, may require workarounds | 99% uptime, limited support hours, basic solutions |
| 1 | Poor | Significant concerns, fails to meet requirements | <99% uptime, poor support, outdated solutions |
5.2 Comprehensive Service Level Agreement (SLA) Framework
A well-defined SLA establishes clear expectations, measurable performance targets, and accountability mechanisms for vendor relationships. The following framework provides a comprehensive template for enterprise-grade SLAs.
Core SLA Components
Service Availability
Definition: Percentage of time service is operational and accessible
Measurement: (Total Scheduled Uptime - Downtime) / Total Scheduled Uptime × 100%
Typical Targets: 99.9% - 99.99% depending on criticality
Performance Metrics
Response Time: Time to acknowledge and begin addressing incidents
Resolution Time: Time to fully resolve service disruptions
Throughput: System capacity and processing capabilities
Support Standards
Incident Classification: P1 (Critical) to P4 (Low) priority levels
Escalation Procedures: Clear escalation paths and timeframes
Communication: Regular status updates and reporting
Security and Compliance
Data Protection: Encryption, access controls, privacy measures
Compliance: Adherence to regulatory requirements
Incident Response: Security incident handling procedures
Detailed SLA Performance Targets
| Service Component | Target Availability | Critical Threshold | Performance Metric | Target Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Core Application Functionality | 99.99% | < 99.95% | Response Time | < 2 seconds |
| Database Access | 99.99% | < 99.95% | Query Response | < 500ms |
| Network Connectivity | 99.99% | < 99.95% | Latency | < 50ms |
| API Endpoints | 99.95% | < 99.90% | Throughput | > 1000 TPS |
| Data Storage Access | 99.99% | < 99.95% | I/O Performance | > 10,000 IOPS |
Incident Response and Support Levels
| Priority Level | Definition | Response Time | Resolution Time | Communication |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 - Critical | Complete service outage or data loss | 15 minutes | 4 hours | Every 30 minutes |
| P2 - High | Significant service degradation | 1 hour | 8 hours | Every 2 hours |
| P3 - Medium | Moderate impact, workaround available | 4 hours | 24 hours | Daily |
| P4 - Low | Minimal impact, enhancement request | 8 hours | 48 hours | Weekly |
SLA Breach Remedies and Penalties
Clear consequences for SLA breaches ensure accountability and provide remedies for service failures:
| Availability Breach | Service Credit | Additional Remedies | Escalation Actions |
|---|---|---|---|
| < 99.95% but ≥ 99.90% | 5% of monthly fees | Root cause analysis | Account manager review |
| < 99.90% but ≥ 99.50% | 10% of monthly fees | Improvement plan required | Executive escalation |
| < 99.50% but ≥ 99.00% | 25% of monthly fees | Service level upgrade | Contract review |
| < 99.00% | 50% of monthly fees | Right to terminate | Legal review |
⚠️6. Risk Management Framework Implementation
A comprehensive risk management framework is essential for identifying, assessing, and mitigating IT-related risks that could impact business operations, security, and compliance.
5.1 Risk Assessment Matrix
The following visual framework helps organizations systematically evaluate and prioritize risks based on their likelihood and potential impact:
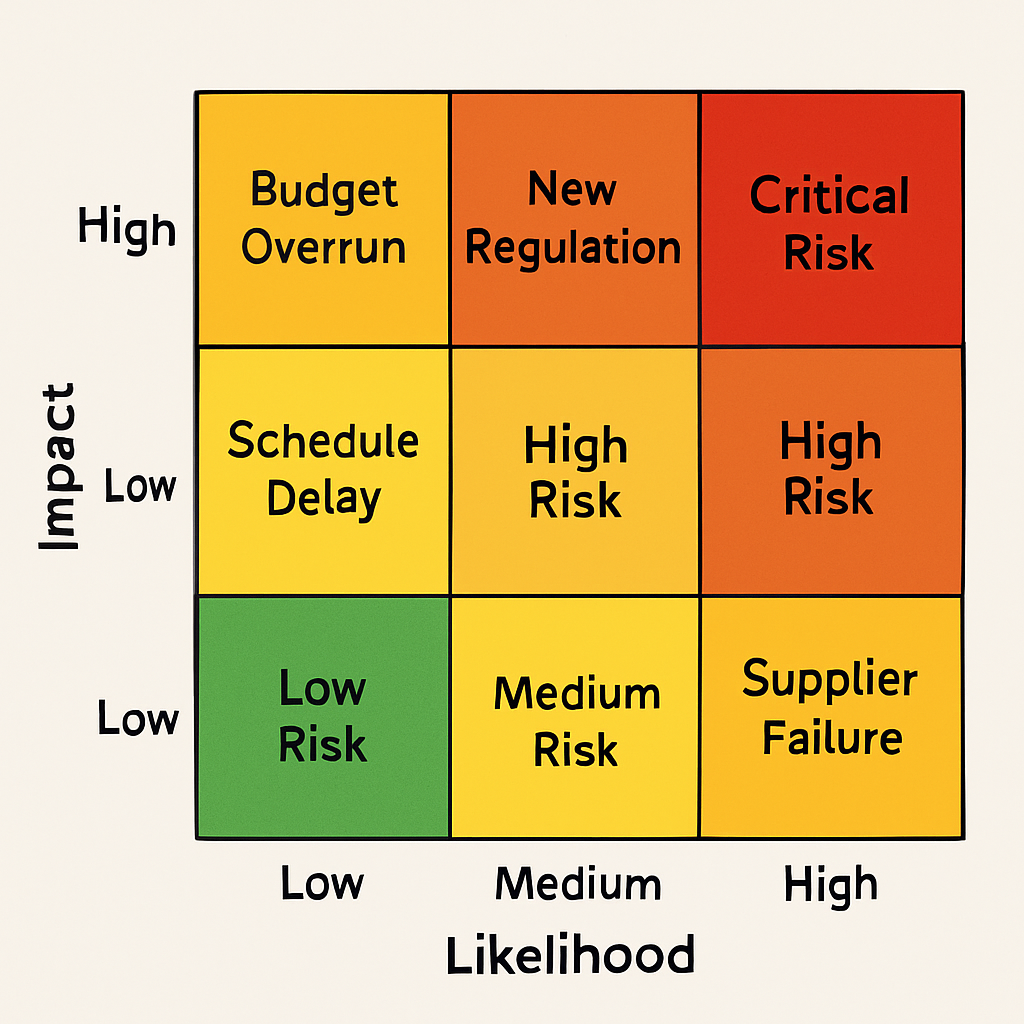
5.2 Risk Management Process
Effective risk management follows a structured process:
5.3 Key Risk Categories in IT Governance
- Cybersecurity Risks - Data breaches, malware attacks, unauthorized access
- Operational Risks - System failures, service disruptions, human errors
- Compliance Risks - Regulatory violations, audit failures, legal penalties
- Strategic Risks - Technology obsolescence, vendor dependencies, budget overruns
- Reputational Risks - Customer trust erosion, brand damage, market perception
📊6. Performance Monitoring and KPI Dashboard
Effective IT governance requires continuous monitoring and measurement of performance against established objectives. A comprehensive KPI dashboard provides real-time visibility into governance effectiveness.
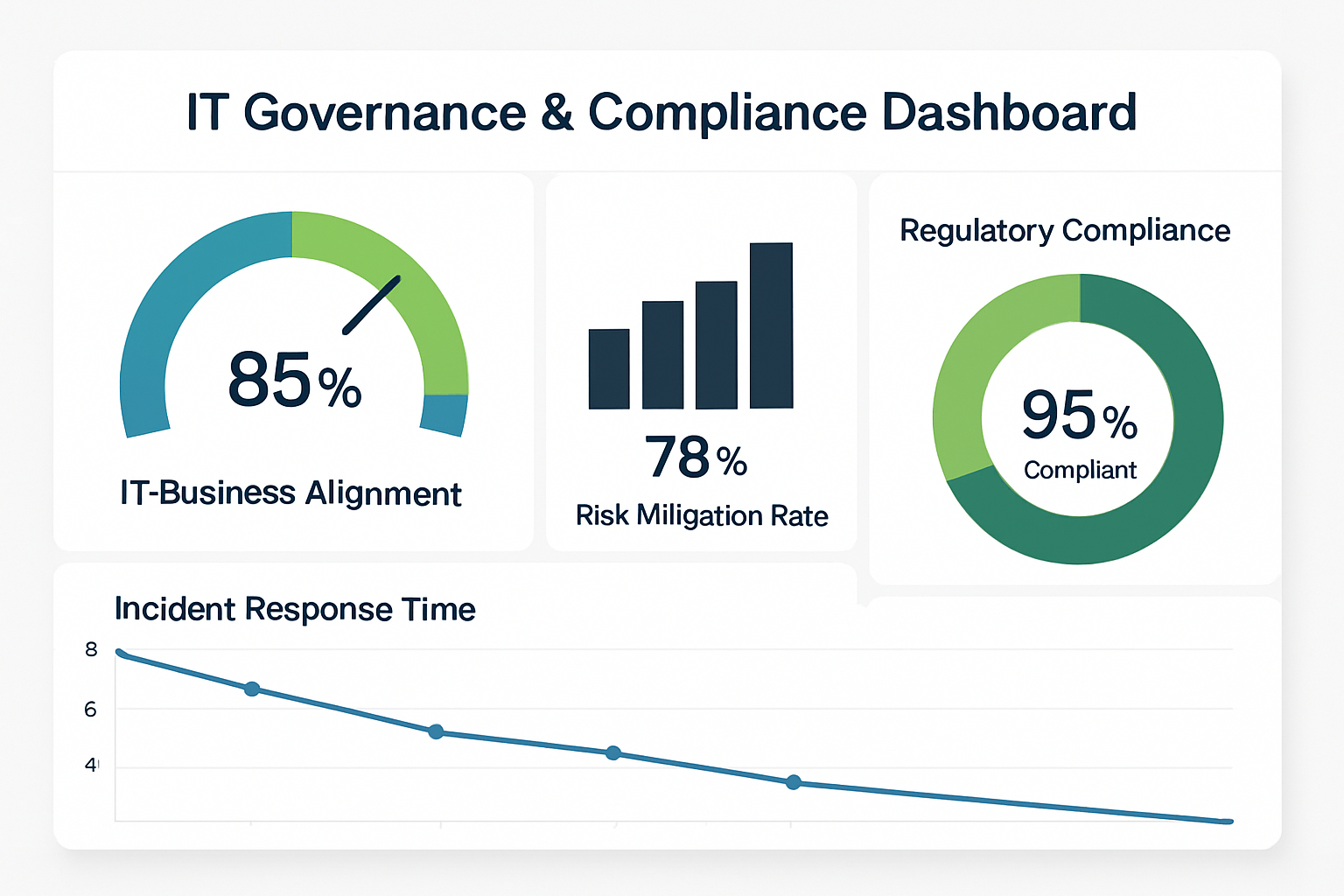
6.1 Key Performance Indicators for IT Governance
| Category | KPI | Target | Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strategic Alignment | % of IT projects aligned with business strategy | > 90% | Quarterly |
| Value Delivery | IT ROI on major investments | > 15% | Annual |
| Risk Management | % of critical risks with mitigation plans | 100% | Monthly |
| Compliance | Audit findings resolution time | < 30 days | Ongoing |
| Performance | System availability | > 99.9% | Daily |
📥7. Downloadable Resources and Templates
To support the practical implementation of your IT governance and compliance framework, we've compiled a comprehensive set of downloadable resources:
Step-by-step implementation guide with timelines, milestones, and stakeholder responsibilities
Comprehensive checklist covering all aspects of governance audit preparation and compliance verification
Detailed assessment tool to evaluate your organization's current governance maturity level across all domains
Ready-to-use template for establishing your IT Governance Committee charter with roles and responsibilities
Collection of essential IT policy templates including AUP, password management, incident response, and data governance
Comprehensive risk tracking spreadsheet with automated risk scoring and mitigation planning features
Structured vendor assessment framework for IT governance decision-making
Comprehensive risk database with industry-specific risk scenarios and mitigation strategies
💡 Implementation Tip
Start with the Governance Charter Template and Maturity Assessment to establish your foundation, then use the Risk Register and Policy Templates to build out your comprehensive framework. The GRC Implementation Roadmap provides the step-by-step guidance to tie it all together.
🚀8. Implementation Roadmap and Best Practices
8.1 Phase-Based Implementation Approach
Implementing a comprehensive IT governance and compliance framework requires a structured, phased approach:
- Establish governance structure and committees
- Define roles, responsibilities, and decision rights
- Conduct current state assessment
- Develop governance charter and initial policies
- Create comprehensive policy library
- Implement risk management framework
- Establish compliance monitoring processes
- Deploy GRC tools and platforms
- Launch performance monitoring and KPI dashboards
- Conduct training and awareness programs
- Implement automated compliance controls
- Establish regular governance reviews
- Regular maturity assessments
- Policy updates and refinements
- Emerging risk identification
- Framework optimization based on lessons learned
🚀9. Implementation Roadmap and Practical Resources
Successfully implementing an IT governance and compliance framework requires a structured approach, proper planning, and practical tools. This section provides a comprehensive implementation roadmap and downloadable resources to support your organization's governance journey.
9.1 Implementation Phases and Timeline
The implementation of a comprehensive IT governance framework follows a phased approach, typically spanning 12-18 months for complete deployment:
| Phase | Duration | Key Activities | Deliverables | Success Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phase 1: Assessment & Planning | 2-3 months | Current state assessment, gap analysis, roadmap development | Governance charter, implementation plan, resource allocation | Executive approval, team formation, budget approval |
| Phase 2: Foundation Building | 3-4 months | Policy development, structure establishment, team training | Core policies, governance structure, training materials | Policy approval, structure operationalization |
| Phase 3: Process Implementation | 4-6 months | Risk management, compliance processes, vendor management | Risk register, compliance framework, vendor assessments | Process deployment, initial risk assessments |
| Phase 4: Monitoring & Optimization | 3-5 months | KPI implementation, dashboard deployment, continuous improvement | KPI dashboard, reporting framework, improvement plans | Operational governance, performance visibility |
9.2 Critical Success Factors
The following factors are essential for successful IT governance implementation:
Executive Sponsorship
Requirement: Visible, active support from C-level executives
Actions: Regular communication, resource allocation, decision authority
Success Indicator: Regular executive participation in governance activities
Stakeholder Engagement
Requirement: Active participation from business and IT stakeholders
Actions: Clear communication, training programs, feedback mechanisms
Success Indicator: High participation rates in governance activities
Adequate Resources
Requirement: Sufficient budget, skilled personnel, and technology tools
Actions: Resource planning, skill development, tool selection
Success Indicator: On-time, on-budget implementation milestones
Change Management
Requirement: Structured approach to organizational change
Actions: Communication plans, training programs, resistance management
Success Indicator: Smooth adoption of new processes and procedures
9.3 Downloadable Implementation Resources
To support your IT governance implementation, we've developed a comprehensive set of professional templates and tools. These resources provide practical frameworks that can be customized for your organization's specific needs:
Professional Implementation Templates
📋 IT Governance Implementation Roadmap
Comprehensive project plan with timelines, milestones, and resource requirements for implementing IT governance framework
Download Excel Template✅ Policy and Audit Checklist
Detailed checklist covering all essential IT policies, compliance requirements, and audit preparation activities
Download Excel Checklist📊 Governance Maturity Assessment
Self-assessment tool to evaluate current governance maturity levels and identify improvement areas
Download Assessment Tool📄 IT Governance Charter Template
Professional Word template for creating your organization's IT governance charter with predefined sections and guidance
Download Word Template📑 Core IT Policy Templates
Complete set of essential IT policy templates including data privacy, security, and asset management policies
Download Policy Pack🎯 Strategic Alignment Framework
PowerPoint presentation template for demonstrating IT-business alignment and governance value proposition
Download Presentation⚡ Quick Implementation Guide
Executive summary guide for rapid governance implementation with key steps and decision points
Download PDF Guide📈 Vendor Evaluation Matrix
Comprehensive vendor assessment spreadsheet with weighted criteria and scoring methodology
Download CSV Template9.4 Advanced Risk Management Resources
Comprehensive risk management tools based on industry best practices and real-world scenarios:
🛡️ Detailed IT Risk Register
Complete risk register with 50+ pre-identified IT risks, assessment criteria, and mitigation strategies
Download Risk Register (CSV)9.5 Implementation Tips and Best Practices
🎯 Quick Start Recommendations
- Start Small: Begin with core policies and gradually expand the framework
- Focus on Value: Prioritize initiatives that deliver immediate business value
- Leverage Existing Processes: Build upon current practices rather than starting from scratch
- Communicate Benefits: Clearly articulate the value proposition to stakeholders
- Measure Progress: Establish baseline metrics and track improvement over time
⚠️ Common Implementation Pitfalls to Avoid
- Over-Engineering: Avoiding overly complex frameworks that hinder adoption
- Lack of Executive Support: Ensuring visible leadership commitment throughout implementation
- Insufficient Training: Providing adequate education and support for all stakeholders
- Poor Communication: Maintaining clear, consistent messaging about goals and benefits
- Ignoring Culture: Addressing organizational culture and change management needs
📈 Measuring Implementation Success
- Adoption Metrics: Track policy compliance rates and process adoption
- Risk Reduction: Monitor decrease in risk scores and incident frequency
- Efficiency Gains: Measure improvements in operational efficiency and decision-making speed
- Stakeholder Satisfaction: Regular surveys to assess user satisfaction and engagement
- Business Value: Quantify the business benefits and ROI of governance investments
🎯10. Conclusion and Key Takeaways
This comprehensive guide has outlined the essential components, frameworks, and practical tools needed to establish robust IT governance and compliance structures in modern enterprise environments. The integration of COBIT 2019 and ITIL 4 frameworks, combined with detailed risk management strategies and vendor governance practices, provides organizations with a complete roadmap for governance excellence.
10.1 Summary of Key Implementation Areas
The successful implementation of IT governance requires attention to eight critical areas:
- Leverage COBIT 2019's 40 governance objectives across five domains
- Implement ITIL 4's Service Value System with seven guiding principles
- Integrate governance system components: processes, structures, policies, information, culture, and competencies
- Develop comprehensive policy library covering all essential IT governance areas
- Establish clear accountability structures and decision rights
- Implement policy lifecycle management with regular reviews and updates
- Deploy structured vendor evaluation using weighted assessment criteria
- Implement comprehensive SLA frameworks with clear performance targets
- Establish enterprise-wide risk management with detailed risk registers and mitigation strategies
- Deploy KPI dashboards for real-time governance visibility
- Implement regular maturity assessments and gap analyses
- Establish continuous improvement processes based on performance data and stakeholder feedback
10.2 Next Steps for Your Organization
To begin your IT governance journey, consider the following immediate action items:
- Download and Review Templates: Start with our comprehensive implementation resources, particularly the Governance Maturity Assessment and Implementation Roadmap
- Conduct Current State Assessment: Evaluate your organization's current governance maturity using the provided assessment tools
- Secure Executive Sponsorship: Present the business case for IT governance using our Strategic Alignment Framework
- Form Implementation Team: Assemble cross-functional team with representatives from IT, Risk, Compliance, and Business units
- Develop Governance Charter: Use our charter template to formalize governance structure and objectives
- Start with High-Impact Areas: Focus initial efforts on risk management and vendor governance for immediate value
10.3 Long-term Benefits and ROI
Organizations that successfully implement comprehensive IT governance frameworks typically realize significant benefits:
Risk Reduction
Typical Results: 40-60% reduction in security incidents, 50-70% improvement in compliance audit results
Operational Efficiency
Typical Results: 25-35% reduction in IT operational costs, 30-50% faster decision-making processes
Strategic Alignment
Typical Results: 80-90% of IT projects aligned with business strategy, improved stakeholder satisfaction
Competitive Advantage
Typical Results: Faster time-to-market for digital initiatives, enhanced customer trust and confidence
- Executive Sponsorship - Ensure strong leadership commitment and visible support from C-level executives
- Cross-Functional Collaboration - Engage stakeholders from IT, Legal, Risk, Compliance, and Business units
- Clear Communication - Maintain transparent communication about objectives, progress, and benefits
- Adequate Resources - Allocate sufficient budget, personnel, and tools for successful implementation
- Change Management - Implement structured change management to ensure adoption and minimize resistance
- Continuous Training - Provide ongoing education and skill development for all stakeholders
🎯 Key Takeaway
Effective IT governance and compliance frameworks require a strategic approach that combines structured governance, comprehensive policies, proactive risk management, and continuous monitoring to ensure technology investments deliver value while maintaining security and regulatory compliance. Success depends on executive commitment, stakeholder engagement, and the use of proven frameworks and practical tools.
"Effective IT governance is not about creating bureaucracy; it's about creating clarity, accountability, and strategic alignment that enables organizations to confidently pursue their digital transformation goals while managing risks appropriately." - Tracy Rivas