Building Organizational Resilience: A Comprehensive Guide to Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity
Executive Summary: In today's interconnected and increasingly unpredictable world, the ability of an organization to withstand, adapt to, and recover from disruptions is paramount. This comprehensive guide provides strategic frameworks, proven methodologies, and practical tools for building organizational resilience through effective disaster recovery and business continuity planning.
Note: This guide includes illustrative diagrams and visual frameworks to enhance understanding of complex BC/DR concepts and relationships.
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Imperative of Organizational Resilience
- Demystifying Disaster Recovery (DR) and Business Continuity (BC)
- Essential Strategies for Developing Comprehensive DR Plans
- Frameworks for Business Continuity Management
- Effective Backup Solutions: Beyond the 3-2-1 Rule
- Ensuring Organization-Wide Resilience
- Conclusion: A Proactive Path to Sustainable Success
🎯 1. Introduction: The Imperative of Organizational Resilience
The modern business landscape is characterized by unprecedented volatility, uncertainty, complexity, and ambiguity (VUCA). Disruptions are no longer rare occurrences but a persistent reality that demands continuous vigilance and adaptation. This fundamental shift in the operating environment means that organizations must transition from a reactive "if a disaster happens" mindset to a proactive understanding that disruptions will occur, frequently and in varied forms.
The Evolving Landscape of Threats
The sheer breadth and increasing frequency of potential threats underscore the critical need for comprehensive preparedness. Cyber threats have proliferated in sophistication, with ransomware, data breaches, and advanced persistent threats posing complex and existential risks to an organization's data integrity, operational continuity, and intellectual property.
Cyber Threats
- Ransomware attacks
- Data breaches
- Advanced persistent threats
- Supply chain attacks
Natural Disasters
- Floods and hurricanes
- Wildfires
- Earthquakes
- Climate change impacts
Economic Disruptions
- Market volatility
- Trade wars
- Supply chain disruptions
- Currency fluctuations
Public Health Crises
- Pandemic responses
- Remote work mandates
- Consumer behavior changes
- Workforce disruptions
The Profound Consequences of Inadequate Preparedness
The ramifications of inadequate preparedness are severe and far-reaching. The most immediate and tangible consequence is financial loss. Prolonged operational downtime directly translates to severe revenue loss, escalating operational costs, and potential penalties for non-compliance with regulatory or contractual obligations.
Financial Impact Statistics:
- $4.88 million: Global average cost of a data breach in 2024 (10% increase from 2023)
- 86 outages: Average number of outages per organization annually
- 55%: Organizations reporting weekly outages
- Power and network issues: Top culprits for expensive outages
🔄 2. Demystifying Disaster Recovery (DR) and Business Continuity (BC)
Understanding the distinct purposes and scopes of Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery, while emphasizing their critical interdependency, is foundational to developing effective preparedness strategies.
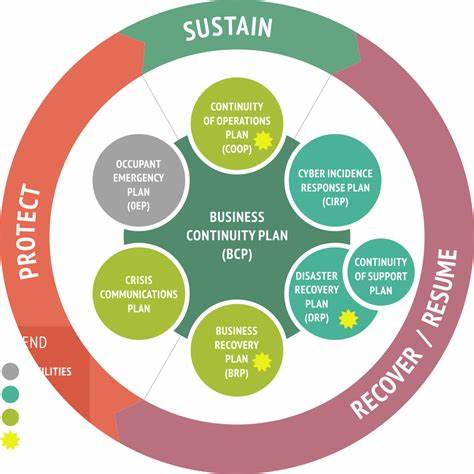
2.1. Business Continuity (BC): Sustaining Operations Amidst Disruption
Business Continuity refers to an organization's overarching ability to continue delivering products and services and maintain essential functions during and immediately following a disruption. The primary goal is to ensure that the business can continue to operate despite various types of disruptions, thereby limiting overall operational downtime.
BC Planning encompasses:
- Staffing: Contingency plans for employee availability, alternate work arrangements, and employee safety
- Communication: Robust internal and external channels to maintain connectivity
- Supply Chain Management: Identifying critical suppliers, diversifying supply sources, and developing contingency plans
- Alternative Procedures: Manual workarounds and resource reallocation strategies
2.2. Disaster Recovery (DR): Restoring Critical IT Systems and Data
Disaster Recovery refers explicitly to the plans and processes for responding to a catastrophic event, with the goal of recovering and restoring critical IT systems and data after a disruption. Its primary objective is to minimize downtime and ensure that IT infrastructure and data are repaired quickly and efficiently.
2.3. The Symbiotic Relationship: Why BC and DR Must Work in Tandem
While distinct in their primary focus, Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery are deeply interdependent and achieve optimal effectiveness when developed and implemented in tandem. The recovery of IT systems and data (DR) is often a prerequisite for the overall continuation of business operations (BC).
Critical Truth: All comprehensive business continuity plans must incorporate robust disaster recovery strategies. However, a standalone DR plan, while critical, does not encompass the full breadth of planning and response required for holistic business continuity.
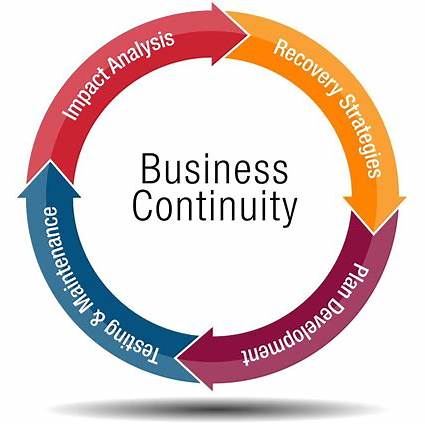
📋 3. Essential Strategies for Developing Comprehensive DR Plans
Developing effective Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery plans requires a structured, systematic approach that moves from foundational analysis to actionable procedures and continuous refinement.
3.1. Risk Assessment and Business Impact Analysis (BIA)
These two interconnected processes form the bedrock of any robust BC/DR plan. They systematically identify potential threats and rigorously quantify their potential impact on the organization.
Risk Assessment Process
Technical Failures
- Server outages
- Hardware failures
- Network disruptions
- Software malfunctions
Cyberattacks
- Ransomware
- Malware infections
- Data breaches
- DDoS attacks
Natural Disasters
- Floods and storms
- Earthquakes
- Wildfires
- Power outages
Human-Made Incidents
- Fire emergencies
- Security incidents
- Supply chain failures
- Economic downturns
Business Impact Analysis (BIA) Framework
The BIA evaluates each potential threat's ramifications across various organizational facets:
| Impact Category | Assessment Criteria | Key Metrics |
|---|---|---|
| Financial Impact | Revenue loss, operational costs, compliance penalties | $ per hour of downtime |
| Operational Impact | Process disruption, productivity loss, customer service | % of capacity affected |
| Reputational Impact | Customer trust, brand value, market position | Customer churn rate |
| Regulatory Impact | Compliance violations, legal liability, audit findings | Penalty amounts |
3.2. Technology-Driven DR Strategies
Cloud-Based Disaster Recovery (DRaaS)
DRaaS Advantages:
- Scalability and Flexibility: Easily scale resources up or down as needed
- Cost-Effectiveness: Reduce capital expenditure with pay-as-you-go models
- Geographic Distribution: Replicate data across diverse cloud regions
- Automated Failover: Significantly reduce RTOs with automated processes
Disaster Recovery Site Types
A disaster recovery (DR) site is a crucial component of a business continuity plan, providing an organization with a secondary location to resume operations and recover critical data and systems following a disaster. These sites are categorized based on their level of readiness, which directly impacts recovery time, cost, and overall operational resilience.
Key Recovery Metrics:
- Recovery Time Objective (RTO): Maximum acceptable time to restore operations
- Recovery Point Objective (RPO): Maximum acceptable data loss measured in time
- Investment Level: Upfront and ongoing costs for maintaining DR capability
🧊 Cold Site
Description: Physical space with essential utilities (power, cooling, network) but no hardware, software, or data.
- RTO: Days to weeks
- RPO: Significant data loss possible
- Cost: Lowest investment
- Best For: Low-priority systems, limited budgets
🔥 Warm Site
Description: Partially equipped with essential hardware and infrastructure, with periodic data synchronization.
- RTO: Hours to days
- RPO: Some data loss (daily/weekly backups)
- Cost: Moderate investment
- Best For: Business-critical applications with some tolerance for downtime
🌡️ Hot Site
Description: Fully functional, redundant facility with real-time data synchronization, ready for immediate failover.
- RTO: Minutes to hours
- RPO: Minimal data loss
- Cost: High investment
- Best For: Mission-critical systems, financial institutions
🪞 Mirrored Site
Description: Real-time, fully redundant replica with instantaneous failover capabilities and zero data loss.
- RTO: Near-instantaneous
- RPO: Zero data loss
- Cost: Highest investment
- Best For: Ultra-high availability requirements
🤝 Reciprocal Agreements
Description: Mutual aid agreements between organizations with similar systems to provide disaster assistance.
- RTO: Unpredictable
- RPO: Unpredictable
- Cost: Low to none
- Risk: High (non-binding, capacity issues)
DR Site Comparison Matrix
| Site Type | RTO | RPO | Investment Level | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cold Site | Days to weeks | Significant | Lowest | Non-critical systems |
| Warm Site | Hours to days | Some | Moderate | Important systems |
| Hot Site | Minutes to hours | Minimal | High | Critical systems |
| Mirrored Site | Near-instantaneous | Zero | Highest | Mission-critical systems |
| Reciprocal Agreement | Unpredictable | Unpredictable | Low to none | Last resort option |
💡 Strategic Considerations:
- Cost vs. Recovery Trade-off: Higher investment yields faster recovery and less data loss
- Hybrid Approaches: Many organizations use tiered DR strategies with different site types for different system criticality levels
- Cloud Integration: Modern DR strategies increasingly leverage cloud platforms for flexible, scalable recovery options
- Testing Requirements: All DR sites require regular testing to ensure functionality and staff readiness
Emerging Technologies in DR
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Predictive failure analysis
- Automated incident response
- Intelligent resource allocation
- Enhanced threat detection
Edge Computing
- Reduced latency for critical operations
- Enhanced local resilience
- Distributed processing capabilities
- Reduced centralized dependencies
Blockchain Technology
- Immutable backup verification
- Secure distributed ledgers
- Smart contract automation
- Enhanced trust and transparency
3.3. Testing and Validation Framework
Regular testing is crucial to ensure the DR plan remains effective, current, and understood by all involved personnel.
| Test Type | Frequency | Success Metrics | Scope |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tabletop | Quarterly | 100% stakeholder participation | Discussion-based plan review |
| Walkthrough | Semi-annually | <5% procedure gaps | Step-by-step verification |
| Simulation | Annually | RTO/RPO targets met | Mock disaster scenarios |
| Full Interruption | Bi-annually | Zero data loss, <15 min failover | Complete failover testing |
📚 4. Frameworks for Business Continuity Management
4.1. ISO 22301: The Global Standard for Business Continuity Management Systems (BCMS)
ISO 22301 is the international standard for Business Continuity Management Systems (BCMS). It provides a comprehensive framework for organizations to plan, establish, implement, operate, monitor, review, maintain, and continually improve a documented management system.
Context & Leadership
- Understanding organizational context
- Leadership commitment
- BC policy establishment
- Role assignments
Planning & Support
- Risk and opportunity identification
- BC objective setting
- Resource provision
- Competence assurance
Operation & Evaluation
- BCMS implementation
- Business impact analysis
- Performance monitoring
- Internal audits
Improvement
- Continual improvement
- Corrective actions
- Management reviews
- System updates
4.2. NIST Cybersecurity Framework Integration
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework's five core functions align well with BC/DR objectives:
| NIST Function | BC/DR Application | Key Activities |
|---|---|---|
| Identify | Asset and risk identification | Inventory critical assets, conduct risk assessments |
| Protect | Preventive controls | Implement access controls, provide training |
| Detect | Monitoring and alerting | Continuous monitoring, anomaly detection |
| Respond | Incident response | Develop response plans, establish communication |
| Recover | Recovery activities | Develop recovery plans, implement improvements |
💾 5. Effective Backup Solutions: Beyond the 3-2-1 Rule
5.1. The 3-2-1-1-0 Backup Strategy
The traditional 3-2-1 rule has evolved into the more comprehensive 3-2-1-1-0 strategy to address modern threats:
5.2. Modern Backup Technologies
Continuous Data Protection (CDP)
- Near real-time data replication
- Point-in-time recovery capabilities
- Minimal data loss (RPO near zero)
- Ideal for mission-critical applications
Snapshot Technology
- Instant point-in-time copies
- Space-efficient storage
- Rapid recovery capabilities
- Short-term recovery needs
Cloud-Native Backup
- Infinite scalability
- Geographic distribution
- Cost-effective retention
- Built-in immutability features
5.3. Backup Performance Monitoring
Backups are only useful if you can restore them on time. Effective backup performance monitoring tracks the right signals to catch problems early, prove compliance with RPO/RTO, and fix bottlenecks before they impact business operations.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Core Backup KPIs with Formulas:
- Job Success Rate = successful jobs ÷ total jobs in window
- Window Compliance = jobs that finished within backup window ÷ scheduled jobs
- Average Throughput = bytes transferred ÷ duration
- Effective Change Rate = bytes transferred ÷ protected dataset size
- RPO Attainment = backups meeting RPO per service ÷ total services
- Restore Success Rate = successful, validated restores ÷ restores attempted
- MTTR (Restore) = end of validation − start of restore
- Immutability Coverage = protected data with immutable retention ÷ protected data total
What to Monitor by Layer
| Monitoring Layer | Key Metrics | Critical Alerts | Business Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Jobs and Policies | Success/failure rates, duration, retries, data processed | Any Tier-1 job failure, window overruns >15% | RPO compliance, SLA breach prevention |
| Capacity and Performance | Repository utilization, throughput, bottleneck identification | Utilization >80%, <14 days to full | Prevents hard stops, maintains performance |
| Security and Resilience | Immutable retention status, access anomalies, restore testing | Any delete events, missed restore tests | Ransomware protection, recovery readiness |
Cloud-Native Telemetry Integration
AWS Backup → CloudWatch
- Backup/restore job metrics (5-min updates)
- EventBridge for delete notifications
- Cross-region monitoring capabilities
- Custom dashboard integration
Azure Backup → Azure Monitor
- Built-in backup health metrics
- Vault-level job counts and coverage
- Direct alert rule creation
- Activity log integration
Google Cloud Backup
- Cloud Monitoring metrics
- Usage and performance tracking
- Automated visualization
- Cloud Logging integration
Troubleshooting Slow Backups
Bottleneck Analysis Framework:
- Target Bottleneck: Repository IOPS limits, dedup storage load, immutability enforcement delays
- Network Bottleneck: Link saturation, high RTT, cross-region or VPN path issues
- Source Bottleneck: Production storage latency, snapshot overhead, application quiescing
- Proxy/Worker Bottleneck: CPU/RAM limits, over-subscribed concurrent tasks
Alerting Thresholds That Matter
| Alert Area | Example Alert | Business Rationale | Response Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Job Health | Any failure on Tier-1 job | Fix before RPO slips | Immediate |
| Window Compliance | Job runtime > window by 15% | Prevents backlog snowball | 4 hours |
| RPO Compliance | No recovery point within RPO | Direct SLA breach | Immediate |
| Security | Any DeleteRecoveryPoint event | Detects destructive activity | Immediate |
| Capacity | Utilization >80% or <14 days to full | Avoids hard stops | 24 hours |
Service Level Objectives (SLOs)
Security and Tamper Resistance Monitoring
Security Monitoring Best Practices:
- Immutability Verification: Regularly verify object lock status and retention coverage
- Access Monitoring: Track backup admin credential usage with MFA requirements
- Change Detection: Alert on any policy modifications or deletion events
- Separate Logging: Send backup logs to independent SIEM environment
- Behavioral Analysis: Monitor for unusual backup system access patterns
5.4. Immutable and Air-Gapped Backups
Modern ransomware threats require advanced backup protection strategies beyond traditional approaches:
Immutable Storage
- Write-once, read-many (WORM) technology
- Object-lock capabilities (e.g., S3 Object Lock)
- Time-based retention policies
- Cryptographic verification
Air-Gap Solutions
- Physical network isolation
- Removable media rotation
- Tape-based long-term storage
- Automated air-gap creation
Zero Trust Backup
- Multi-factor authentication for recovery
- Least-privilege access models
- Continuous verification
- Encrypted communication channels
5.5. Advanced Recovery Strategies
| Recovery Strategy | RTO Range | RPO Range | Cost Level | Best Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Active-Active | 0-5 minutes | 0-1 minute | High | Mission-critical systems |
| Active-Passive | 5-30 minutes | 1-15 minutes | Medium-High | Critical business applications |
| Warm Standby | 30 minutes - 4 hours | 15 minutes - 1 hour | Medium | Important business systems |
| Cold Standby | 4-24 hours | 1-8 hours | Low-Medium | Non-critical systems |
| Backup Restore | 24-72 hours | 8-24 hours | Low | Development, testing systems |
🏢 6. Ensuring Organization-Wide Resilience
6.1. Building a Culture of Resilience
Leadership and Governance
Governance Structure Elements:
- Executive Sponsorship: C-level champion for resilience initiatives
- Steering Committee: Cross-functional leadership team
- Program Manager: Dedicated BC/DR program leadership
- Technical Teams: Recovery, continuity, and communications specialists
Training and Awareness Program
Executive Level
- Strategic decision-making
- Crisis communication
- Program oversight
- Resource allocation
Management Level
- Team coordination
- Resource management
- Procedure implementation
- Departmental planning
Employee Level
- Emergency procedures
- Individual responsibilities
- Incident reporting
- Safety protocols
Technical Level
- System recovery
- Data restoration
- Failover processes
- Technical troubleshooting
6.2. Supply Chain Resilience
| Risk Category | Assessment Criteria | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Geographic | Single location dependency | Diversify suppliers across regions |
| Financial | Supplier financial stability | Regular financial reviews, alternative suppliers |
| Operational | Single source dependencies | Alternative sourcing, buffer inventory |
| Cyber | Security posture | Security assessments, standards adherence |
6.3. Measuring Resilience Maturity
| Level | Characteristics | Key Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| 1 - Initial | Ad-hoc, reactive approaches | No documented plans, reactive responses only |
| 2 - Developing | Basic plans in place | Some documented procedures, limited testing |
| 3 - Defined | Documented processes | Formalized plans, regular testing, defined roles |
| 4 - Managed | Metrics-driven approach | KPI measurement, continuous improvement |
| 5 - Optimized | Predictive capabilities | Proactive risk management, industry leadership |
🎯 7. Conclusion: A Proactive Path to Sustainable Success
Building organizational resilience through effective disaster recovery and business continuity planning is no longer optional—it's a business imperative. In an era defined by escalating cyber threats, climate events, and global disruptions, organizations that proactively invest in these capabilities are better positioned to protect their assets, minimize downtime, and ensure continuity of operations.
Key Success Factors: Success requires a holistic approach that combines robust technical solutions with strong governance, comprehensive testing, and a culture of resilience. Organizations that integrate BC/DR into their broader enterprise risk management framework will gain significant competitive advantage.
Strategic Recommendations
Executive Action Items:
- Establish Executive Sponsorship: Assign C-level leadership for resilience initiatives
- Implement Comprehensive Testing: Regular drills and validation exercises
- Invest in Modern Technologies: Cloud-based DR, AI-driven monitoring, automation
- Build Resilient Culture: Training, awareness, and continuous improvement
- Integrate with ERM: Align BC/DR with enterprise risk management
The goal isn't to prevent all disruptions—it's to ensure your organization can quickly adapt, recover, and continue serving stakeholders regardless of the challenges faced. Organizations that master these elements will be better positioned to leverage resilience as a competitive advantage and drive sustainable business growth in an increasingly volatile world.
🔧 8. Practical Tools and Resources
Based on industry best practices and proven frameworks, the following tools and resources can significantly accelerate your BC/DR implementation:
8.1. Essential Assessment Tools
Business Impact Analysis (BIA) Template
- Critical process identification
- RTO/RPO target setting
- Impact quantification
- Dependency mapping
Risk Assessment Matrix
- Threat identification framework
- Probability vs. impact analysis
- Risk prioritization
- Mitigation strategy planning
Recovery Checklist Generator
- Step-by-step procedures
- Role-based responsibilities
- Validation checkpoints
- Communication protocols
Exercise Planning Template
- Scenario development
- Testing schedules
- Success metrics
- Improvement tracking
8.2. Implementation Lifecycle
Proven Implementation Approach:
- Assessment Phase: Complete BIA and risk assessment using standardized templates
- Strategy Development: Design recovery strategies aligned with business objectives
- Plan Documentation: Create comprehensive, testable procedures
- Implementation: Deploy technical solutions and train personnel
- Testing & Validation: Conduct regular exercises and measure effectiveness
- Continuous Improvement: Refine based on test results and changing requirements
8.3. Advanced Analytics and Monitoring
| Metric Category | Key Performance Indicators | Target Values | Measurement Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Backup Performance | Success rate, completion time, storage utilization | >99.5%, | Daily |
|
| Recovery Readiness | RTO achievement, RPO compliance, test success rate | Meet targets, Zero data loss, >95% success | Monthly |
| Plan Currency | Document updates, contact verification, procedure validation | Quarterly updates, 100% verification, Annual validation | Quarterly |
| Training Effectiveness | Participation rate, competency scores, exercise performance | 100% participation, >90% scores, Improving trends | Semi-annually |
8.4. Regulatory and Compliance Considerations
Key Compliance Frameworks Integration:
- FFIEC BCM Guidelines: Financial services resilience requirements
- GDPR Article 32: Security of processing and incident response
- HIPAA Security Rule: Healthcare data protection and recovery
- SOX Section 404: Internal controls over financial reporting
- PCI DSS Requirement 12.10: Incident response plan implementation
🚀 9. Future Trends and Emerging Technologies
9.1. AI-Driven Recovery Automation
Predictive Analytics
- Failure pattern recognition
- Proactive resource scaling
- Anomaly detection systems
- Capacity planning optimization
Automated Response
- Intelligent failover decisions
- Dynamic resource allocation
- Self-healing systems
- Orchestrated recovery workflows
9.2. Zero Trust Architecture Integration
Modern BC/DR strategies must integrate with Zero Trust security principles, ensuring that recovery processes maintain security posture while enabling rapid restoration of services.
9.3. Quantum-Resistant Encryption
As quantum computing advances, organizations must prepare for post-quantum cryptography requirements, ensuring that backup encryption remains secure against future threats.
Future-Proofing Recommendation: Develop modular BC/DR architectures that can accommodate emerging technologies while maintaining backward compatibility with existing systems and processes.
References and Further Reading
- IBM. (2024). Cost of a Data Breach Report 2024. Retrieved from https://www.ibm.com/reports/data-breach
- Morgan Lewis. (2025, May 14). Study Finds Average Cost of Data Breaches Significantly Increased Globally in 2024.
- Uptime Institute. (2024). Annual Outage Analysis 2024.
- Invenio IT. (2025, April 28). 25 Disaster Recovery Statistics Every Business Should Know.
- ISO. (2019). ISO 22301:2019 - Business continuity management systems.
- NIST. NIST Cybersecurity Framework. Retrieved from https://www.nist.gov/cyberframework
- NIST. (2010). NIST SP 800-34 Rev. 1 - Contingency Planning Guide for Federal Information Systems.
- Disaster Recovery Institute International (DRII). Professional Practices for Business Continuity Management.
- TRG Datacenters. Disaster Recovery Site Types: Understanding Your Options.
- AWS. Disaster Recovery of Workloads on AWS: Recovery in the Cloud.
- CISA. Data Backup Options. Retrieved from https://www.cisa.gov/sites/default/files/publications/data_backup_options.pdf
- FFIEC. Business Continuity Management Guidelines. Retrieved from https://www.ffiec.gov
- ISO/IEC. (2025). ISO/IEC 27031:2025 - Information technology — Security techniques — Guidelines for ICT readiness for business continuity.
- TechTarget. (2025, February 25). 6 ways to use AI in IT disaster recovery.
- DBTA. (2025, June 18). AI in Disaster Recovery: Mapping Technical Capabilities to Real Business Value.
- Business Continuity Institute. Good Practice Guidelines. Retrieved from https://www.thebci.org
- FEMA. Continuity Guidance Circular. Retrieved from https://www.fema.gov/emergency-managers/national-preparedness/continuity
- Veeam. (2024). Data Protection Trends Report 2024.